Showing 6 of 1754 Results

Institute NewsMay 6, 2025
Read MoreWelcoming rising stars in science to Sanford Burnham Prebys
The annual Rising Stars Symposium featured nine doctoral-degree candidates representing the next generation of scientists.
Institute NewsMay 5, 2025
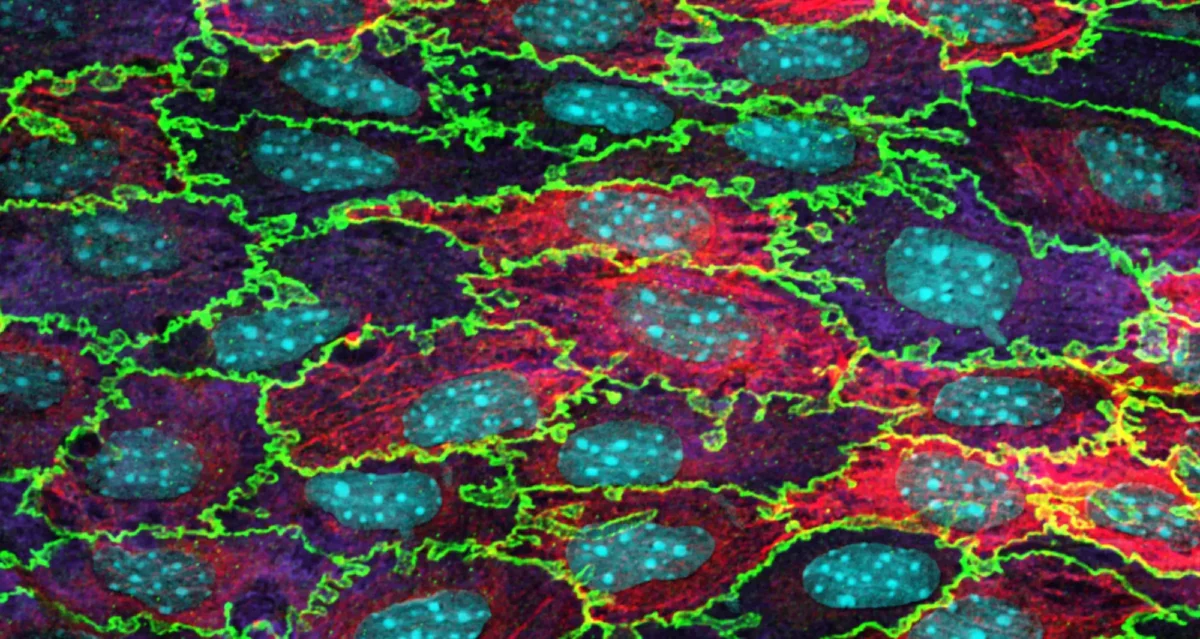
Science in Pictures
A weekly image series featuring selected pictures in science • Mouse aortic endothelium

Press ReleaseMay 5, 2025
CIAO Study: A long and ongoing look at the secrets of human longevity and healthy aging
This month, researchers participating in the Cilento Initiative on Aging Outcomes or CIAO study will gather in Acciaroli Salerno, Italy…
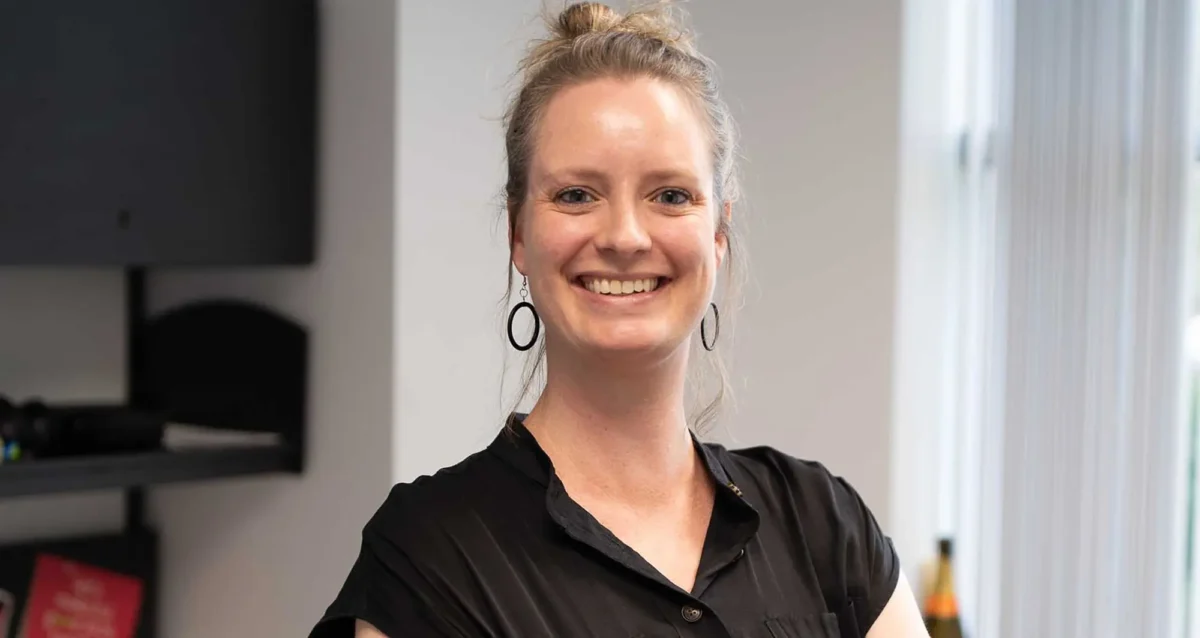

Institute News
Kelly Kersten awarded Melanoma Research Alliance grant to support research on melanoma immunotherapy
May 2, 2025
Institute NewsApr 28, 2025
Science in Pictures
A weekly image series featuring selected pictures in science • Myelinated axons

Institute NewsApr 25, 2025
Hot and Freeze
We’re on Radiolab! Hudson Freeze, PhD, joins the legendary science podcast to recount a discovery that changed biology forever.
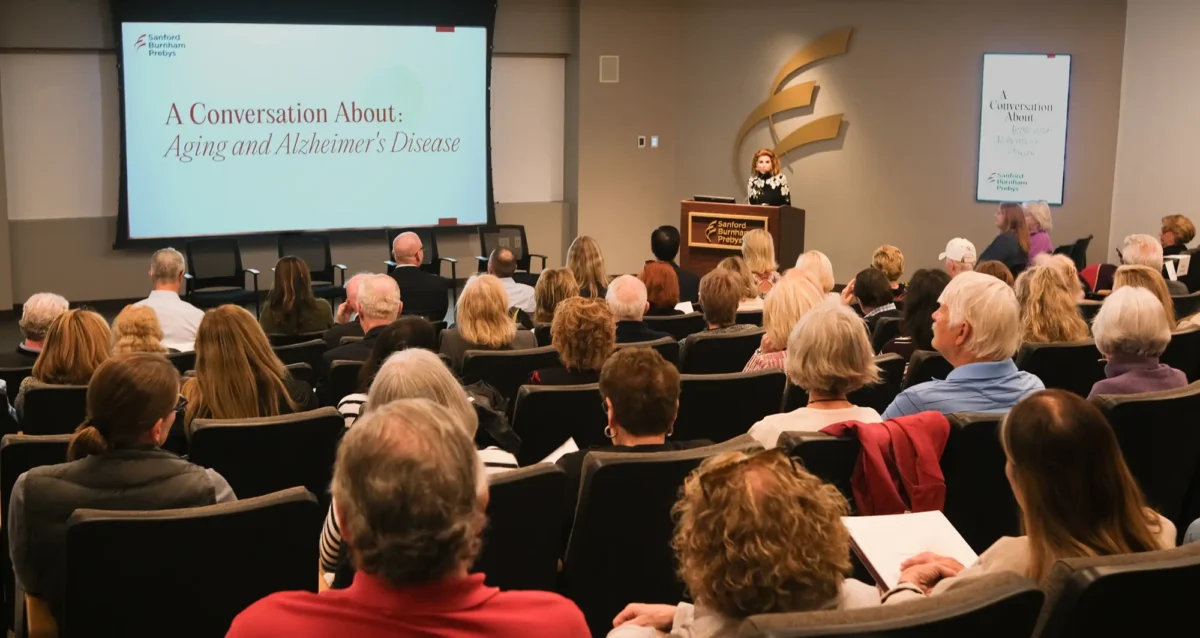

Institute NewsApr 23, 2025
A Conversation About Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease at Sanford Burnham Prebys
The Institute recently welcomed members of the community for an engaging afternoon focused on the intersection of aging and Alzheimer’s…
