Alessandra Sacco completed her studies at La Sapienza University in Rome, Italy. In 2002, Dr. Sacco joined the laboratory of Prof. Helen M. Blau at Stanford University as a postdoctoral fellow (2002-2009), where she studied cell fusion between hematopoietic cells and muscle cells, as a potential mechanism for tissue repair. Recently she defined strategies to isolate adult skeletal muscle stem cells and performed single cell transplantation experiments, providing the first definitive evidence that adult muscle stem cells are able to self-renew in vivo. She received research funding from Muscular Dystrophy Association (2006-2008). In 2010, Dr. Sacco was recruited as Assistant Professor at Sanford Burnham Prebys.
Related Disease
Childhood Diseases, Muscular Dystrophy, Sarcopenia/Aging-Related Muscle Atrophy
Skeletal muscle wasting is a devastating pathology that occurs in several human conditions, including muscular dystrophies, aging, and HIV. There is currently no cure for it. Muscle stem cells offer great promise for future therapies, but their use is currently limited by our poor understanding of the regulatory mechanisms directing their behavior. We are interested in understanding how extrinsic and intrinsic factors regulate muscle stem cells in vivo. Current projects include:
- Developing stem cell-based strategies for treating muscle wasting diseases
- Understanding how aging affects the muscle stem cell compartment.
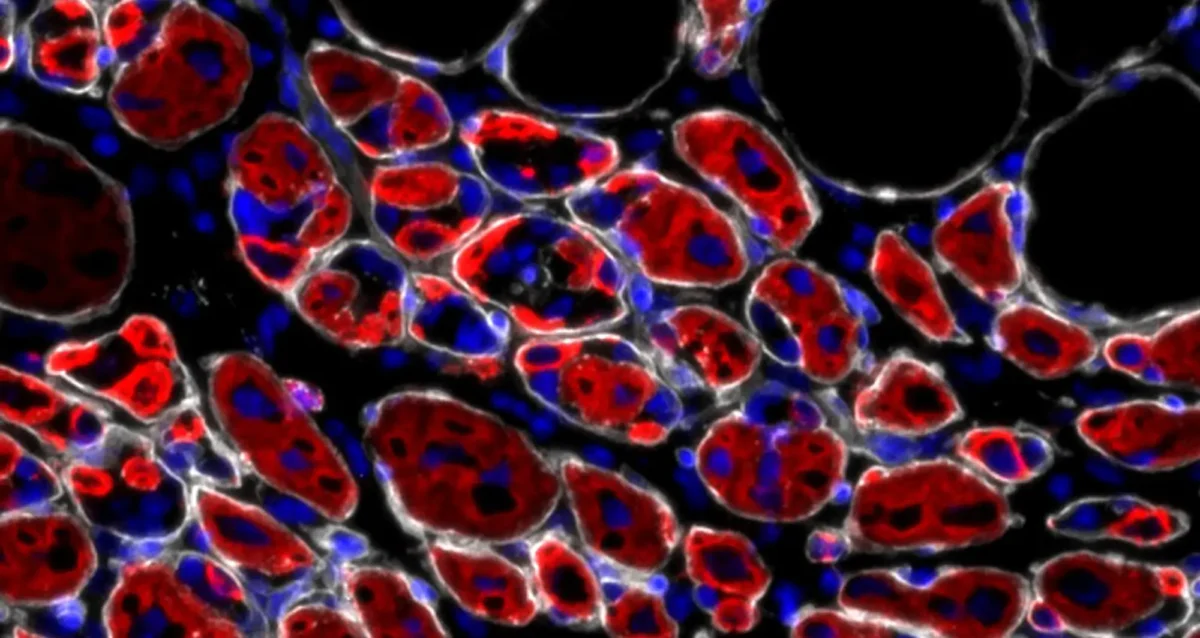 Dec 5, 2025
Dec 5, 2025Protein puppeteer pulls muscle stem cells’ strings
Dec 5, 2025Study from the Sacco lab links the tenascin-C protein to muscle stem cell levels and muscle regeneration, may lead to…
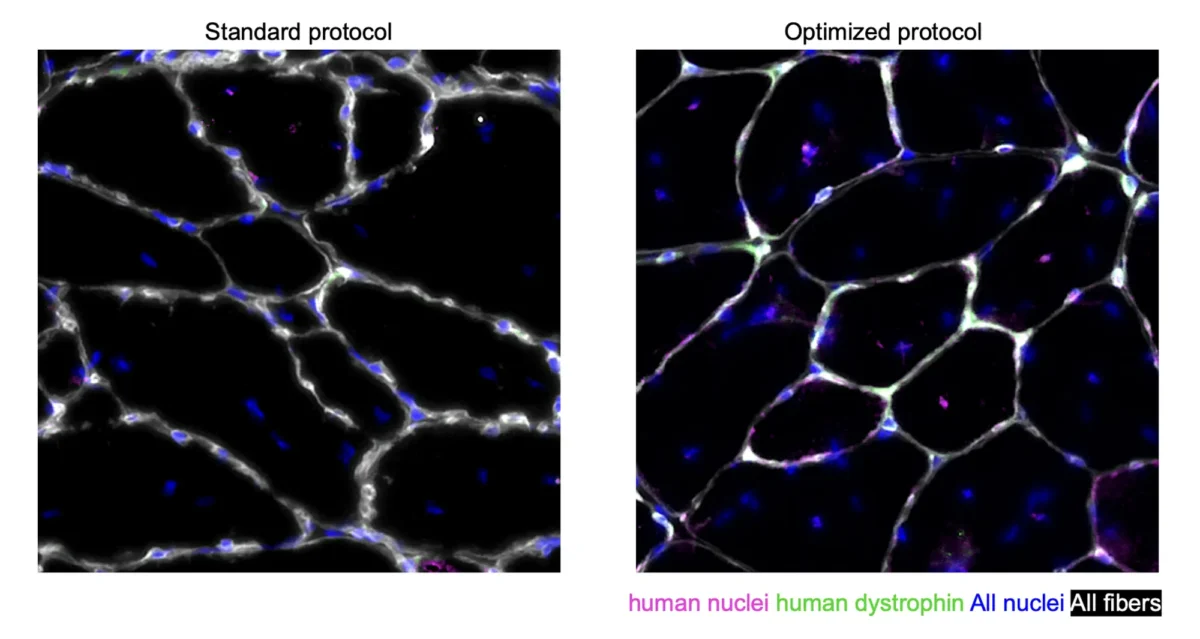 Oct 30, 2025
Oct 30, 2025Making more supply to meet the demands of muscle cell therapy
Oct 30, 2025Study shows that blocking a protein can yield more and more potent cells for regenerating diseased muscle.
 Apr 1, 2025
Apr 1, 2025Experts exchange advances in the science of healthier aging in San Diego
Apr 1, 2025Two scientific meetings in late March brought together researchers studying aging and its implications for disease.
 Mar 12, 2025
Mar 12, 2025Registration open for San Diego aging research meetings in March
Mar 12, 2025Register by March 17 for two exciting opportunities to learn more about aging research conducted in San Diego and beyond.
 Aug 19, 2024
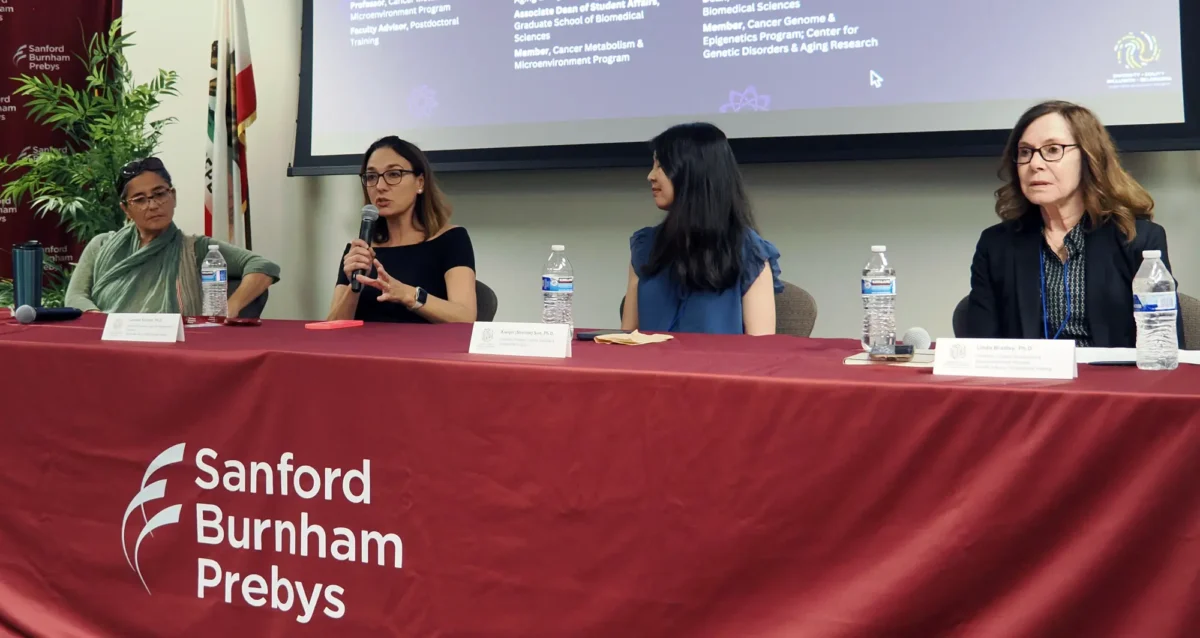
Aug 19, 2024Women in Science event at Sanford Burnham Prebys examines how female faculty members navigate research careers
Aug 19, 2024Topics at the event included work/life balance, caregiving and family obligations, and gender disparities in academic rank at research and…
 Jun 7, 2024
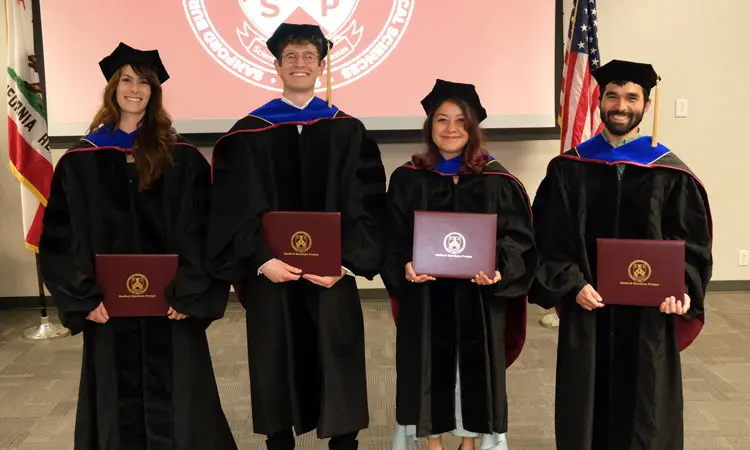
Jun 7, 2024Sanford Burnham Prebys celebrates first graduate school Commencement ceremony
Jun 7, 2024The Sanford Burnham Prebys Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences held its first-ever Commencement ceremony to celebrate nearly 20 years of…
