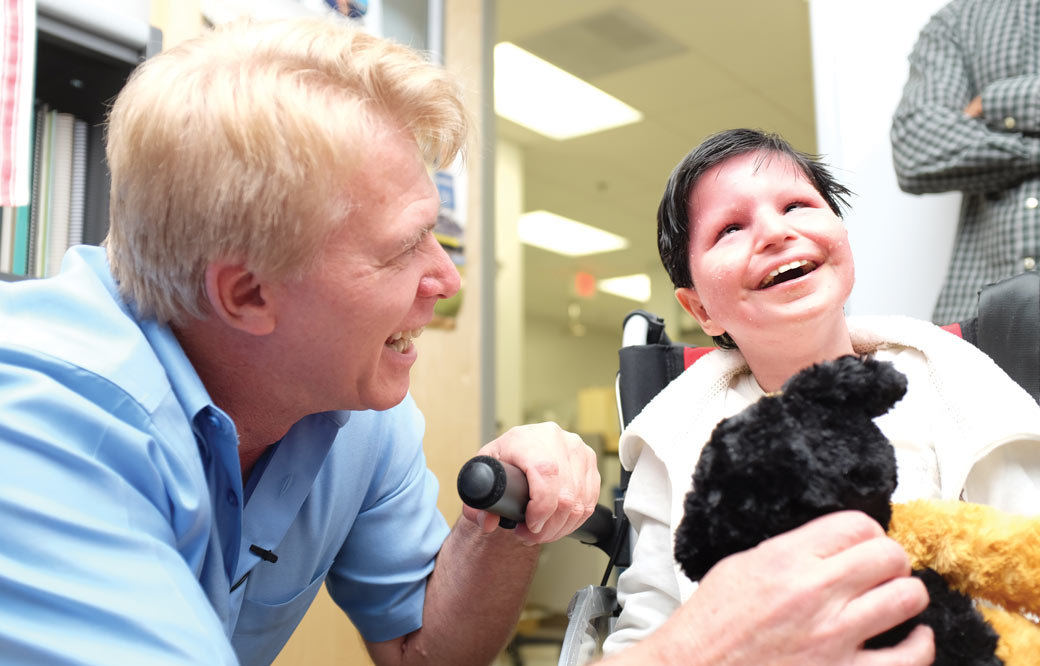
Hudson Freeze, PhD, professor of Human Genetics at Sanford Burnham Prebys, has joined a historic effort that establishes—for the first time—a nationwide network of 10 regional academic centers, Sanford Burnham Prebys researchers and patient advocacy groups to address decades of unresolved questions surrounding congenital disorders of glycosylation, or CDG, a rare disease that affects children. The consortium is funded by a $5 million, five-year grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
“We are extremely pleased that the NIH is investing in an initiative that will improve the lives of people affected by CDG,” says Freeze, who leads efforts to develop and validate disease biomarkers that will aid in diagnoses, and measuring treatment benefits during clinical trials. “Although globally the number of people living with CDG is relatively small, the impact on the lives of these individuals and their families can be profound. We look forward to working with the patients, families, physicians, scientists and other stakeholders focused on this important study.”
CDG is caused by genetic mutations that disrupt how the body’s sugar chains attach to proteins. First described in the 1990s, today scientists have discovered more than 140 types of mutations that lead to CDG. Symptoms are wide-ranging, but can include developmental delays, movement problems and impaired organ function. Some children may benefit from a sugar-based therapy; however, developing treatments for those who need alternative treatment options has been hindered by a lack of natural history data—tracking the course of the condition over time—comprehensive patient registry, and reliable methods to establish the CDG type.
Working together, the consortium will overcome these hurdles by:
- Defining the natural history of CDG through a patient study, validating patient-reported outcomes and sharing CDG knowledge
- Developing and validating new biochemical diagnostic techniques and therapeutic biomarkers to use in clinical trials
- Evaluating whether dietary treatments restore glycosylation to improve clinical symptoms and quality of life
Freeze will lead the efforts to develop and validate biomarkers for CDG, working alongside the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and the Mayo Clinic. The principal investigator of the CDG Consortium Project is Eva Morava, MD, PhD, professor of Medical Genetics at the Mayo Clinic. The patient advocacy groups involved are CDG CARE and NGLY1.org.
Sanford Burnham Prebys and CDG Care will host the 2020 Rare Disease Day Symposium and CDG Family Conference from February 28 to March 1 in San Diego, which welcomes researchers, clinicians, children with CDG and their families, and additional CDG community members. Register to attend.