A career history of fundamental discovery and translational research in immunology has guided Dr. Ware to identify new drug targets and develop novel therapeutics. Dr. Ware’s career in immunology and virology began in 1982 when he became a Professor at the University of California, Riverside’s Division of Biomedical Sciences. In 1996, he joined the La Jolla Institute for Immunology in San Diego as Head of the Division of Molecular Immunology. Professor Ware joined Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute in 2010, serving as the Director of the Infectious and Inflammatory Disease Center and Adjunct Professor of Biology at the University of California at San Diego. He is currently the Director of the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology, which focuses on discovering and designing immunotherapeutics.
As an educator, he taught medical students immunology and virology. He trained over 60 postdoctoral fellows and graduate students who chose careers in research in academic and pharmaceutical science, patent law, or teaching.
Dr. Ware advises scientific panels and review boards for the National Institutes of Health and serves on the scientific advisor boards for the Allen Institute for Immunology and the Arthritis National Research Foundation. Scientific advisor with several biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies on immunotherapy for cancer and autoimmune diseases using innovative approaches to target discovery and drug development.
Dr. Ware’s research program is dedicated to unraveling the intricate intercellular communication pathways that govern immune responses. His work, which centers on cytokines in the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) Superfamily, particularly those that regulate cell survival and death in response to viral pathogens, spans the domains of cancer,autoimmune and infectious diseases.
At Sanford Burnham Prebys, Dr. Ware is pivotal in promoting the translation of the faculty’s scientific discoveries. His efforts have led to the Institute’s reputation as a productive and preferred partner in collaborations with Pharma, including multi-year research and drug development projects with Eli Lilly and Avalo Therapeutics. His success translating fundamental knowledge into rational drug design has led to three novel therapeutics targeting inflammatory pathways, currently in clinical trials.
Education
1981-1982: T cell Immunology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute of Harvard Medical School in Boston, MA. Tim Springer and Jack Strominger, advisors.
1979-1981: Biochemistry of Complement, University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX. W Kolb, advisor
1974-1979: PhD in Molecular Biology and Biochemistry from the University of California, Irvine; Gale Granger, PhD mentor.
Honors and Recognition
Distinguished Fellow, American Association of Immunologists
Honorary Lifetime Membership Award International Cytokine and Interferon Society
Hans J. Muller-Eberhardt Memorial Lecture
Biotech All Star, San Diego Padres Awar
“Pillars of Immunology” discovery of the Lymphotoxin-b Receptor, published in Science
Outstanding Alumnus, Ayala School of Biological Sciences, University of California, Irvine
National MERIT Award R37 (10 years), National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease, NIH
National Research Service Award, NIH Postdoctoral Fellowship
Related Disease
Arthritis, Breast Cancer, Cancer, Crohn’s Disease (Colitis), Infectious Diseases, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Inflammatory/Autoimmune Disease, Inherited Disorders, Leukemia/Lymphoma, Myeloma, Pathogen Invasion, Psoriasis, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Type 1 Diabetes
Research in the Laboratory of Molecular Immunology is directed at defining the intercellular communication pathways controlling immune responses. Our work is focused on the Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-related cytokines in regulating decisions of cell survival and death, especially in responses to viral pathogens. Translational research is redirecting the communication networks of TNF superfamily to alter the course of autoimmune and infectious disease and cancer.
Carl Ware’s Research Report
Discovery of the TNF-LIGHT-LTαβ Network
The molecular elements of this cellular communication network were revealed with our discovery of Lymphotoxin-β and its formation of the trimeric heterocomplex with LTαβ1 and its signaling receptor, Lymphotoxin-β Receptor2. The LTβR revealed a new inter-cellular communication pathway that provides a key mechanism underlying the development and homeostasis of lymphoid organs. A second ligand we discovered, LIGHT (TNFSF14), is a novel ligand for the herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM; TNFRSF14), and surprisingly, the LTβR3 heralding the concept that TNF, LTαβ, and LIGHT form an integrated signaling network thru distinct receptors controlling inflammation and host defense.4
LTβR Signaling in Host Defense and Immune Evasion
Our investigations into the mechanisms of virus evasion of the immune system revealed an essential role of the LTβR pathway in regulating the type 1 interferon response to cytomegalovirus5 and now recognized as a major defense against other pathogens. LTβR signals differentiate macrophages and stromal cells into IFN-producing cells. LTβR transcriptomics and proteomics datasets we generated revealed a novel constellation of anti-viral host defense mechanisms6. Importantly the role of the LTβR pathway to alter tissue microenvironments by differentiation of specialized stromal cells has implications for promoting effective immune responses to cancer.
Discovery of the HVEM-BTLA Immune Checkpoint
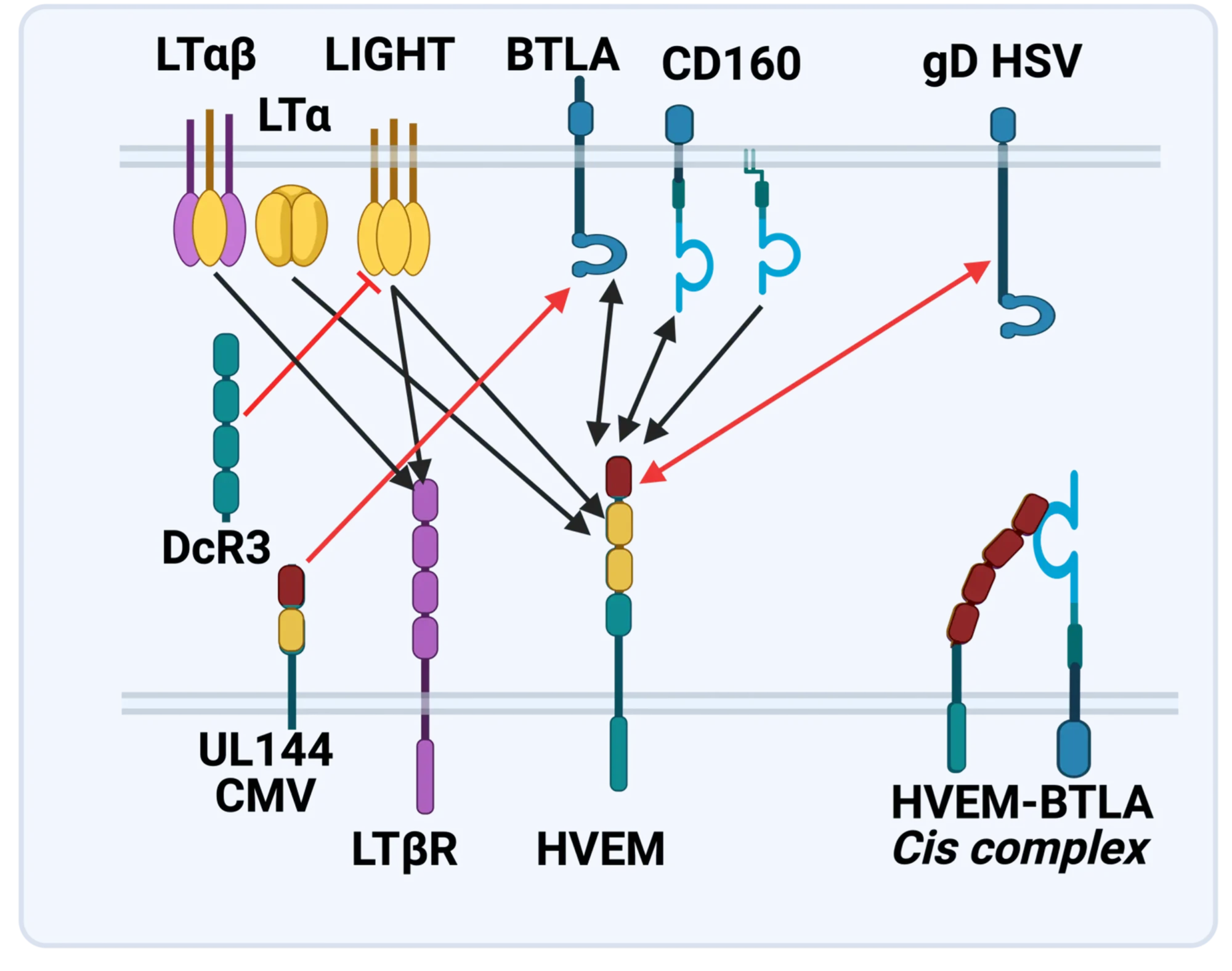
The LTBR-HVEM-BTLA Network in the TNF Superfamilies. Arrows indicate ligand-receptor binding (black), inhibitors (red arrow) and bidirectional signaling (dual arrowheads); HSV, herpes simplex virus; CMV, human cytomegalovirus. BTLA and CD160 are Ig Superfamily proteins. BTLA is an inhibitory checkpoint receptor; DcR3, decoy receptor 3 inhibits LIGHT binding to HVEM and LTBR.
The discovery that HVEM is a coreceptor for the immune checkpoint, B and T lymphocyte attenuator (BTLA), an Ig superfamily member, established a new paradigm in TNF Receptor signaling pathways 7. Additional investigations revealed the importance of the HVEM-BTLA system in limiting immune responses, including T cell help for B cell clonal expansion, antibody maturation, and secretion8. HVEM-BTLA also regulates control of the intestinal microbiome, limiting invasion of pathogenic bacteria and enhancing Treg cell homeostasis 9. The diverse roles of this pathway are seen in the loss of BTLA signaling from mutations in HVEM frequently present in B cell lymphomas10. Additional layers of immune regulators, CD160 and DcR3, control the LIGHT-HVEM-BTLA pathways, revealing this network as a key mechanism controlling immune homeostasis.
Appreciating the fundamental features of the TNF-LIGHT-LTab Network in effector and homeostasis mechanisms presents a target-rich resource for therapeutic intervention in autoimmunity, infection, and cancer11, 12.
Translational research and Immunotherapy
- 2021-current: Lead Scientific Advisor, Avalo Therapeutics
A neutralizing, fully human mAb (quisovalimab) to the proinflammatory cytokine LIGHT (TNFSF14) completed Phase I with an excellent safety profile and a Phase II trial establishing efficacy in COVID-19 pneumonia (NCT0441205)13. We identified elevated serum levels of LIGHT in hospitalized patients with COVID1914 spurring a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, proof-of-concept trial with adults hospitalized with COVID-19-associated pneumonia and mild to moderate ARDS15. The results established efficacy with a significant proportion of patients remaining alive and free of respiratory failure through day 28 after receiving quisovalimab, most pronounced in patients >60 years of age (76.5% vs. 47.1%, respectively; P = 0.042). These results and animal models validated LIGHT as a target for non-COVID inflammatory conditions, clinical trials ongoing in asthma (NCT05288504)12. - 2021-current: Principal Investigator, Avalo Therapeutics – Sanford Burnham Prebys collaboration
Bioengineered a first-in-class checkpoint agonist targeting BTLA immune checkpoint16 in preclinical development - 2019-current: Director and Principal Investigator, Fair Journey Biologics – Sanford Burnham Prebys collaboration
Immunotherapy for TNBC and PANC, in preclinical development - 2015-2022: Director and Lead Principal Investigator, LILLY-Sanford Burnham Prebys Collaboration in Autoimmunity
Collaborative research partnership with Eli Lilly involved target discovery and therapeutic development directed at immune regulators for autoimmune diseases. The collaboration produced three novel biologics currently in Phase I/2 trials (NCT03933943). The collaboration included a target discovery platform for T cell effector memory and NK cell immunomodulators. - 2015-2020: Lead Principal Investigator, Sanford Burnham Prebys – Capella Biosciences collaboration
Created a fully human mAb specific for membrane LIGHT (CBS001); phase I initiated (NCT05323110). - 2016-2020: Lead Scientific Investigator, Boehringer Ingelheim – Sanford Burnham Prebys Collaboration
Target discovery collaboration in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases6 - 2012-2014: Pfizer Innovation Center, Principal Investigator Bioengineering TNFR Superfamily in Autoimmune disease
- 1. Browning, J.L. et al. Lymphotoxin beta, a novel member of the TNF family that forms a heteromeric complex with lymphotoxin on the cell surface. Cell 72,847-856 (1993).
- 2. Crowe, P.D. et al. A lymphotoxin-beta-specific receptor. Science 264,707-710 (1994).
- 3. Mauri, D.N. et al. LIGHT, a new member of the TNF superfamily, and lymphotoxin alpha are ligands for herpesvirus entry mediator. Immunity 8,21-30 (1998).
- 4. Ward-Kavanagh, L.K., Lin, W.W., Sedy, J.R. & Ware, C.F. The TNF Receptor Superfamily in Co-stimulating and Co-inhibitory Responses. Immunity 44,1005-1019 (2016).
- 5. Schneider, K. et al. Lymphotoxin-mediated crosstalk between B cells and splenic stroma promotes the initial type I interferon response to cytomegalovirus. Cell Host Microbe 3,67-76 (2008).
- 6. Virgen-Slane, R. et al. Cutting Edge: The RNA-Binding Protein Ewing Sarcoma Is a Novel Modulator of Lymphotoxin beta Receptor Signaling. J Immunol 204,1085-1090 (2020).
- 7. Sedy, J.R. et al. B and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates T cell activation through interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator. Nat Immunol 6,90-98 (2005).
- 8. Mintz, M.A. et al. The HVEM-BTLA Axis Restrains T Cell Help to Germinal Center B Cells and Functions as a Cell-Extrinsic Suppressor in Lymphomagenesis. Immunity 51,310-323 e317 (2019).
- 9. Stienne, C. et al. Btla signaling in conventional and regulatory lymphocytes coordinately tempers humoral immunity in the intestinal mucosa. Cell reports 38,110553 (2022).
- 10. Sedy, J.R. & Ramezani-Rad, P. HVEM network signaling in cancer. Adv Cancer Res 142,145-186 (2019).
- 11. Croft, M., Benedict, C.A. & Ware, C.F. Clinical targeting of the TNF and TNFR superfamilies. Nat Rev Drug Discov 12,147-168 (2013).
- 12. Ware, C.F., Croft, M. & Neil, G.A. Realigning the LIGHT signaling network to control dysregulated inflammation. J Exp Med 219 (2022).
- 13. Zhang, M., Perrin, L. & Pardo, P. A Randomized Phase 1 Study to Assess the Safety and Pharmacokinetics of the Subcutaneously Injected Anti-LIGHT Antibody, SAR252067. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 6,292-301 (2017).
- 14. Perlin, D.S. et al. Levels of the TNF-Related Cytokine LIGHT Increase in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients with Cytokine Release Syndrome and ARDS. mSphere 5 (2020).
- 15. Perlin, D.S. et al. Randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of human anti-LIGHT monoclonal antibody in COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest 132 (2022).
- 16. Sedy, J.R. et al. A herpesvirus entry mediator mutein with selective agonist action for the inhibitory receptor B and T lymphocyte attenuator. J Biol Chem 292,21060-21070 (2017).
 Mar 25, 2025
Mar 25, 2025Engineering antibodies with a novel fusion protein
Mar 25, 2025Fusing two immune system proteins leads to a new method of generating antibodies and may advance drug discovery.
 Nov 19, 2024
Nov 19, 2024Protein superfamily crucial to the immune system experiences Broadway-style revival
Nov 19, 2024San Diego scientists note a resurgence of interest in research on protein family to find new drug candidates.
 Jun 1, 2023
Jun 1, 2023Pumping the brakes on autoimmune disease
Jun 1, 2023New study describes the science behind an autoimmune disease treatment in a Phase 2 clinical trial Researchers at Sanford Burnham…
 Nov 2, 2022
Nov 2, 2022Seeing the immune system in full color
Nov 2, 2022A new flow cytometer at the Institute will help researchers study the immune system with unprecedented resolution and speed. The…
 Apr 6, 2022
Apr 6, 2022How our immune system controls gut microbes
Apr 6, 2022And how this relationship could help fight autoimmune diseases
 Jan 20, 2022
Jan 20, 2022New COVID-19 drug passes phase 2 clinical trial
Jan 20, 2022The new treatment, developed by Avalo Therapeutics with Sanford Burnham Prebys researchers, can mitigate lung damage and improve survival in…
