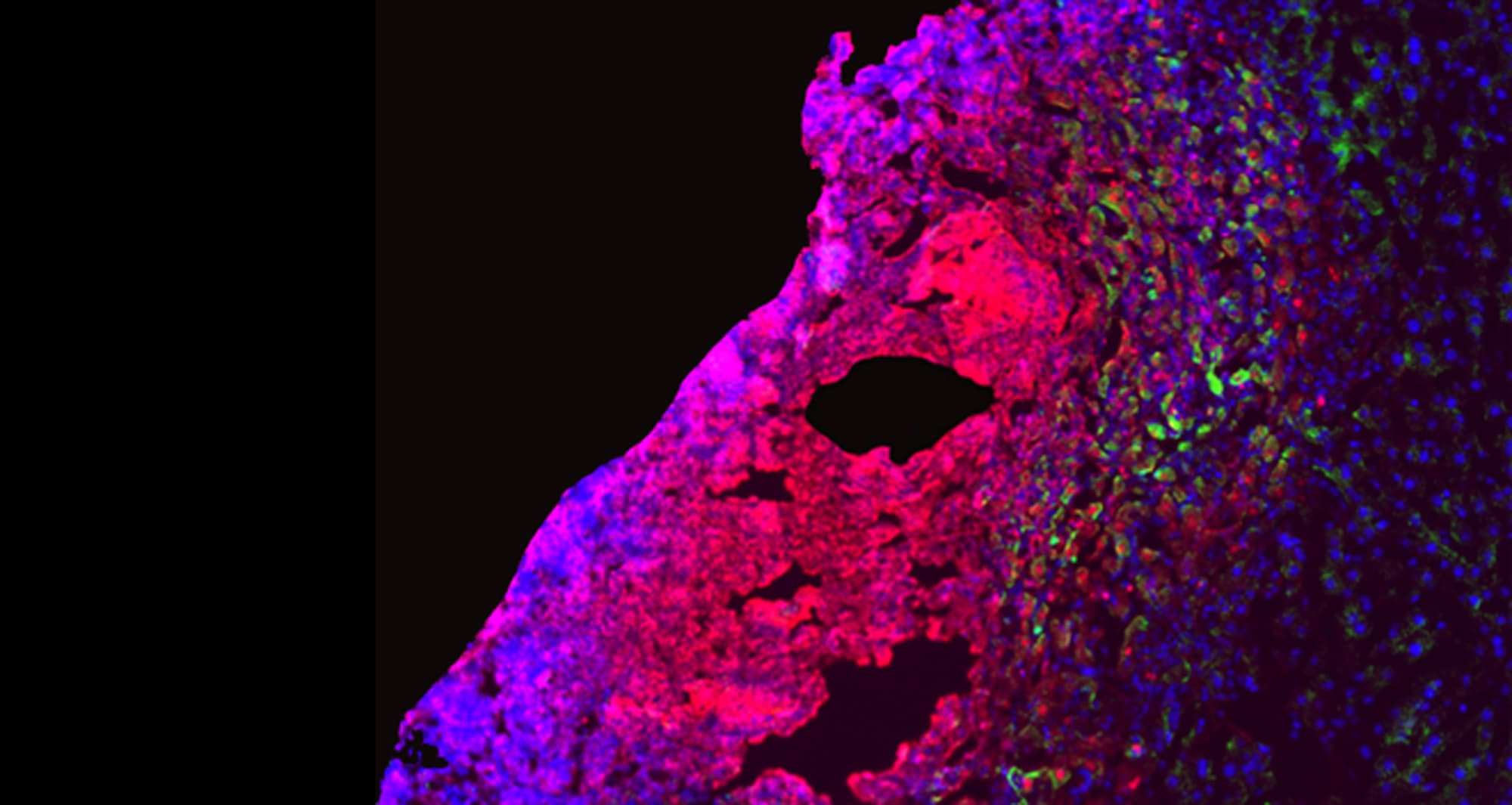
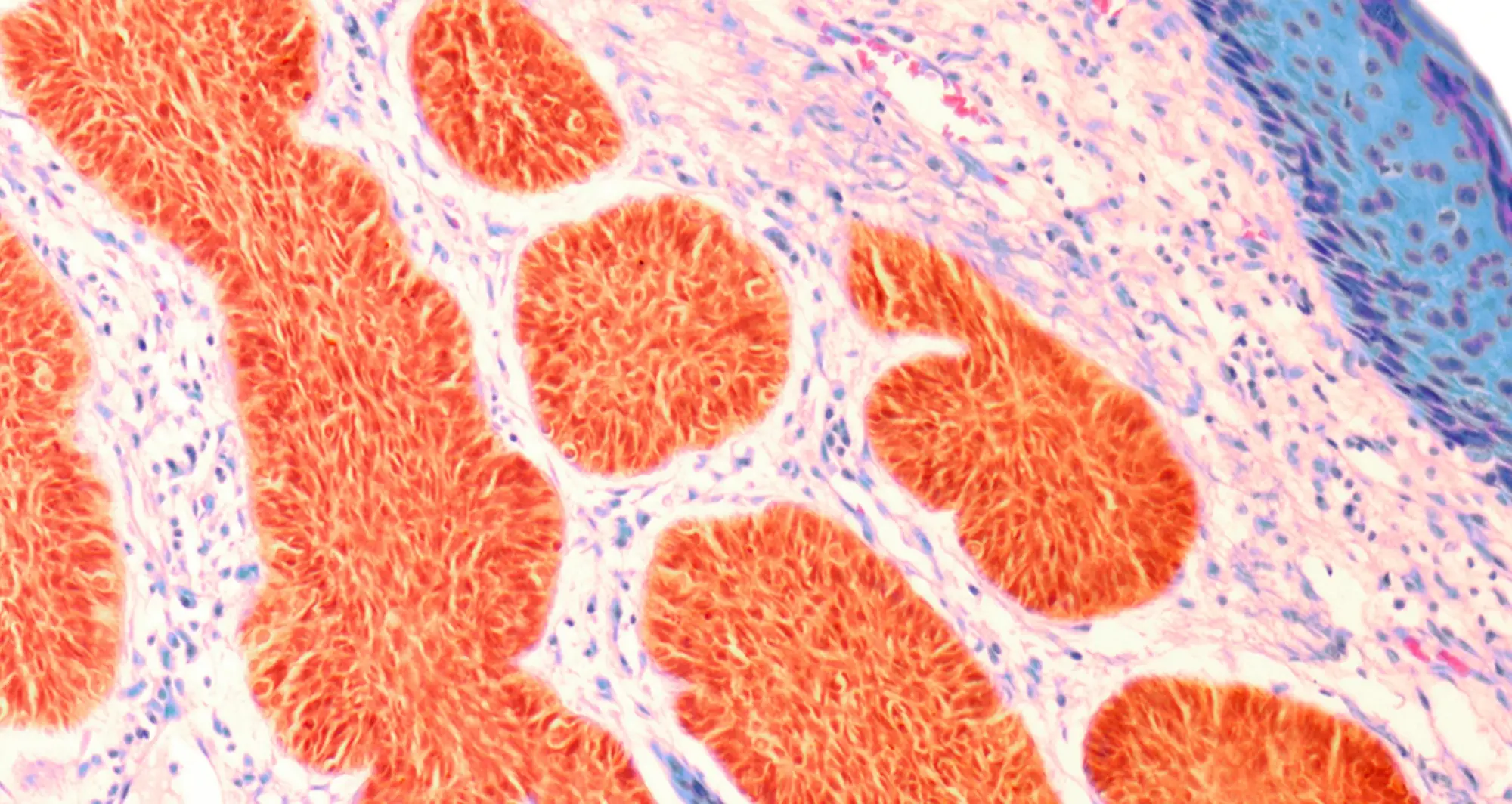
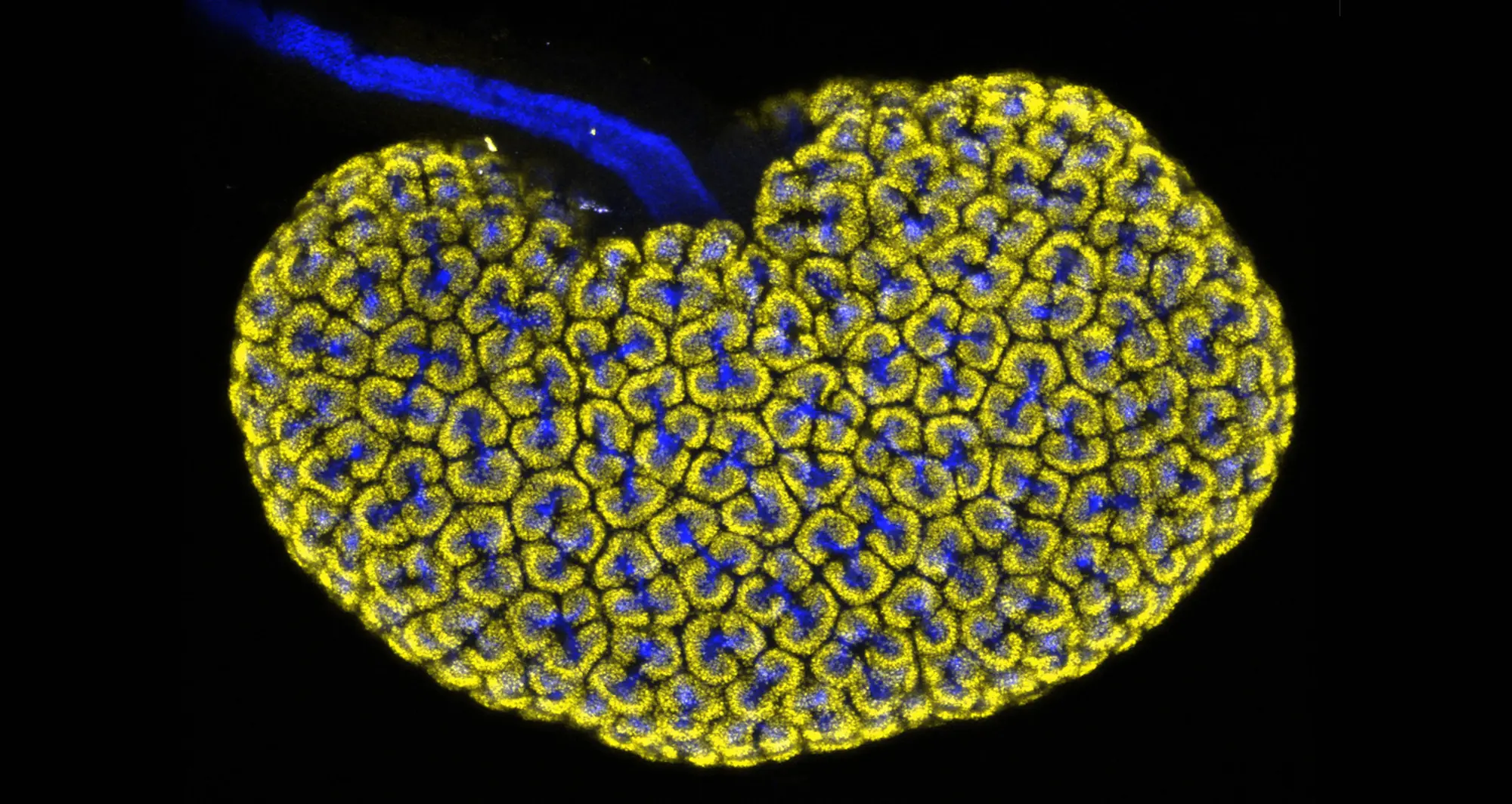
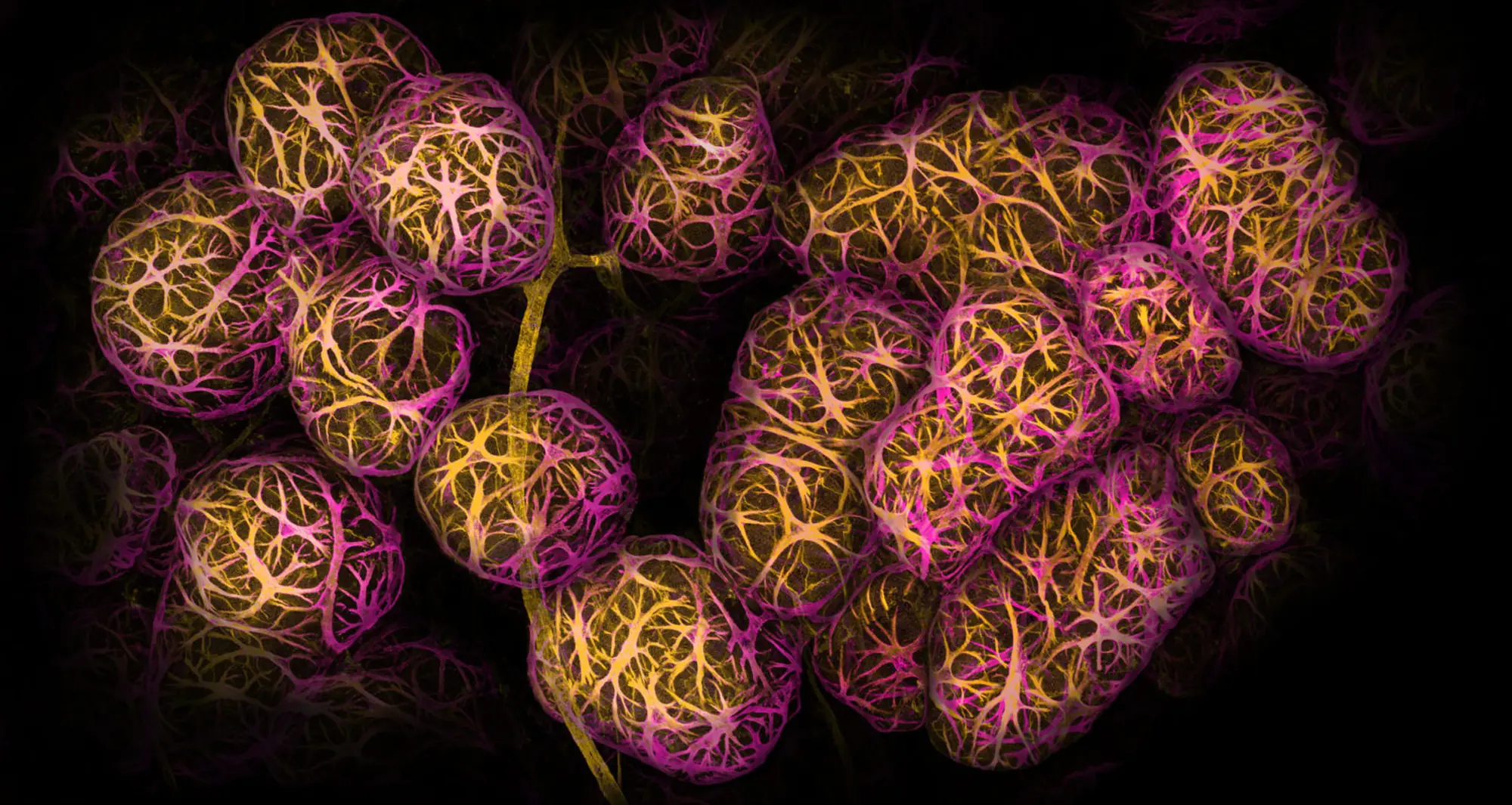
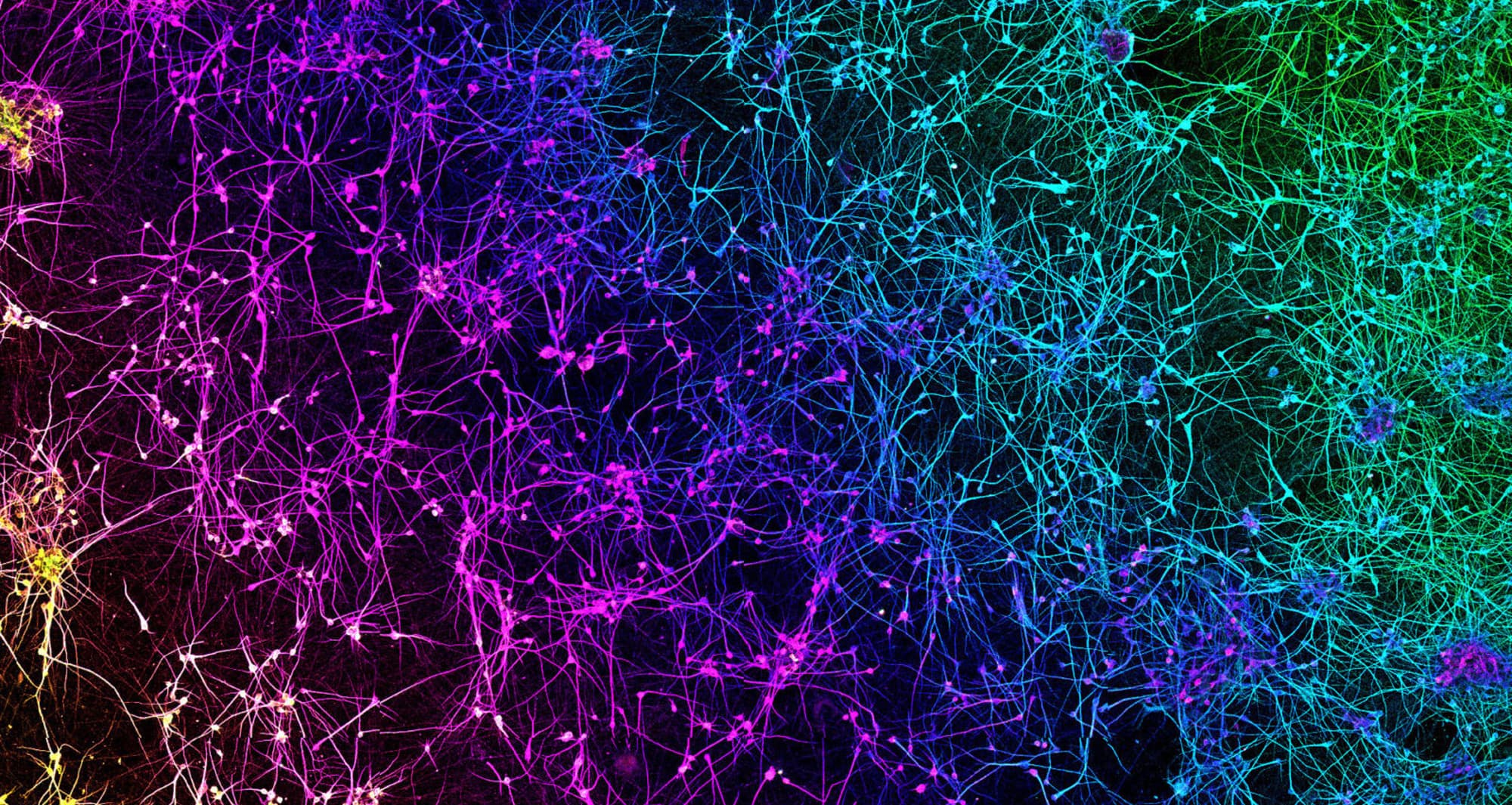
In this micrograph of a liver lesion from a mouse infected with Chromobacterium violaceum, some cells are dying (red) while other healthy cells (blue) are activating a protein (green) to fight the bacteria.
Image courtesy of Edward Miao at Duke University and Vivien Maltez at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.