New editorial recommends a multimodal perspective examining glioblastoma from tumor biology through to surgery
Glioblastoma is one of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant forms of brain cancer. It also is the most common form of cancer that originates in the brain, making research into new and better therapies even more imperative.
Physician–scientist Theophilos Tzaridis, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute in the lab of Peter Adams, PhD, recently surveyed promising glioblastoma studies after being invited to serve as a guest editor for a special issue of Frontiers in Oncology and Frontiers in Neurology.
More exact and safe surgeries
Tzaridis highlighted two studies focused on improving surgery for glioblastoma, as it continues to be the primary treatment for the disease. The recent publications discussed how to enhance the use of MRI to map out tumors and surrounding tissue, as well as other innovative mapping and monitoring techniques. These approaches would enable neurosurgeons to create better and safer plans for reducing risk of recurrence and avoiding side effects before starting surgery.
Targeted treatments and immunotherapies
Scientists have sought to add treatment options for glioblastoma beyond surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Some other cancers can be treated with targeted therapies that exploit a unique characteristic of certain tumors, but this approach has yet to yield long-term successes for glioblastoma patients. Tzaridis brought forward a case report of a patient whose tumors were nearly completely cleared by a targeted therapy after chemotherapy was unsuccessful. He suggests that future studies are warranted to identify patient subpopulations that can benefit from these treatments.
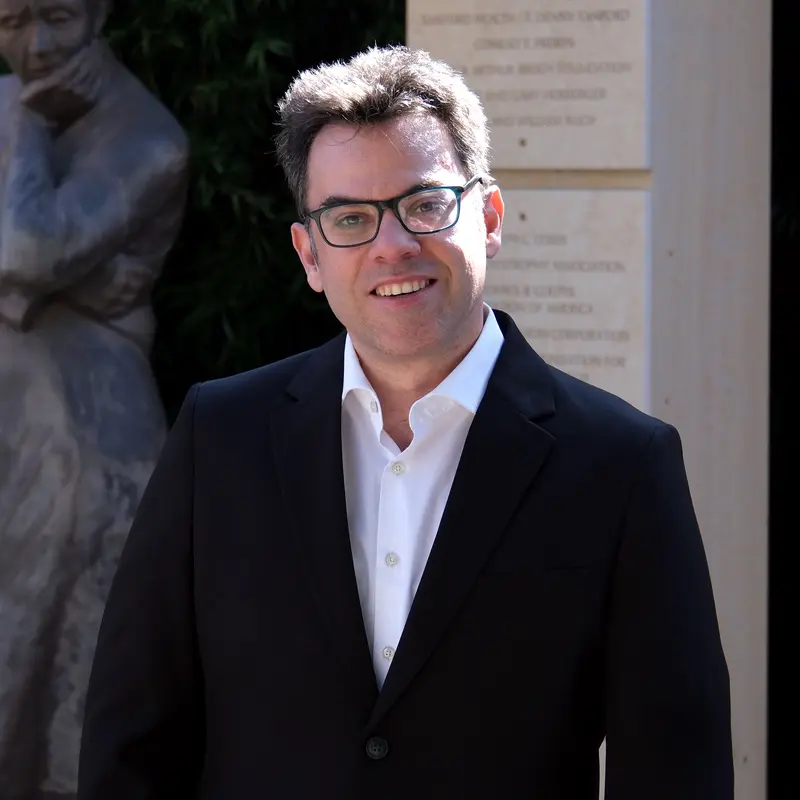

Theophilos Tzaridis, MD, a postdoctoral fellow at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute. Image credit: Sanford Burnham Prebys.
Immunotherapies that supercharge the immune system to better detect and eliminate cancer have transformed the treatment of many blood cancers and solid tumors. It has not, however, yet born fruit as an effective treatment for glioblastoma. Tzaridis spotlights a study discussing the potential use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) natural killer (NK) cells in glioblastoma rather than the more common CAR T-cell therapies.
The blood brain barrier and brain cancer biology
In addition to demonstrating how research is contributing to improving existing treatments and finding new potential therapies, Tzaridis emphasized the importance of continued studies of brain cancer cell biology and the obstacle to treatment posed by the blood brain barrier. He highlighted two studies focused on overcoming the blood brain barrier along with another two studies regarding cellular models and the use of extracellular vesicles to package and deliver treatments.
“With a multimodal perspective from addressing challenges in neurosurgery to improving our understanding of tumor biology and achieving therapeutic delivery into the brain, we have the best chance of improving survival of patients with this devastating disease,” said Tzaridis.