Anne Bang, PhD, focuses her research on bridging stem cell technology and drug discovery to enable the development of therapeutics. She was trained in developmental neurobiology and used both invertebrate and vertebrate models to study mechanisms that underlie spatial patterning of the nervous system in the developing embryo.
Bang’s experience with human pluripotent stem cells (hPSC) began in 2005 when she joined ViaCyte, Inc., as Director of Stem Cell Research, she led an interdisciplinary group developing hPSC-derived pancreatic cells to treat diabetes. Her efforts focused on optimizing differentiation processes and advancing Viacyte’s cell product into scaled manufacturing and studies enabling Investigational New Drug (IND) applications for the FDA. This work led to co-inventorship on multiple ViaCyte patents.
In 2010, Bang joined Sanford Burnham Prebys to lead hPSC-based disease modeling at the Conrad Prebys Center for Chemical Genomics (Prebys Center), a state-of-the-art drug discovery center. Her program leverages hPSC technology to generate disease-relevant models across different genetic backgrounds and differentiated lineages, enabling interrogation of cellular vulnerabilities and pathogenic phenotypes in human cells.
A central premise of Bang’s work is that these models are impactful when paired with quantitative, scalable phenotyping and systematic perturbation with small molecules, genetic modulation or other stressors to identify pathway-level control points and therapeutic hypotheses. Accordingly, her laboratory develops stem-cell-based assays that capture higher-order cellular and network functions while maintaining throughput compatible with discovery. Her team developed and ran an image-based, high-content screening platform in iPSC-derived neurons to identify chemical modulators of neurite outgrowth (Sherman and Bang, 2018), as well as a phenotypic screen in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patient iPSC neurons that uncovered a druggable CYP46A1–cholesteryl ester–tau axis linking neuronal cholesterol metabolism to core AD pathologies (van der Kant et al., 2019).
To extend screening beyond morphology to systems-level function, she and her colleagues built multi-electrode array (MEA) workflows for iPSC-derived neuronal networks and have generated compound-response signatures across >270 perturbagens, including seizure-relevant phenotypes (in prep), alongside analytic methods to map network connectivity (Puppo et al., 2021). They further advanced MEA-based functional phenotyping by developing assays to model synaptic plasticity via long-term potentiation (LTP) (Pré et al., 2022) and to quantify oscillogenesis, emergent network dynamics and their pharmacological modulation, in scalable hPSC-derived cortical cultures (Pré et al., 2026).
Related Disease
Aging-Related Diseases, Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (Lou Gehrig’s Disease), Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation, Glycosylation-Related Disorders, Multiple Sclerosis, Muscular Dystrophy, Neurodegenerative and Neuromuscular Diseases
Phenomena or Processes
Cell Biology, Development and Differentiation, Development of Neuronal Circuits, Embryonic/Pluripotent Stem Cells, Neurobiology, Neurodegeneration, Neurogenesis, Neuron-Glia Interactions in Myelin, Neurotransmitters, Synapse Formation and Maturation, Synapse Function, Synaptic Transmission
Research Models
Human Adult/Somatic Stem Cells, Human Cell Lines, Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Techniques and Technologies
Cellular and Molecular Imaging, Drug Discovery, Electrophysiology, Fluorescence Microscopy, High Content Imaging, In vivo Modeling, Microarrays, Molecular Genetics
Dr. Anne Bang is an experienced cell biologist and stem cell expert who leads efforts at the Prebys Center to develop patient cell specific and human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC)-based disease models for drug screening and target identification. Her research program is primarily focused on neurological and neuromuscular disease, with the aim of designing human cell based models and assays that reflect higher order cellular functions and recapitulate disease phenotypes, yet have the throughput and reproducibility required for drug discovery. Towards this goal, her group has worked to develop a suite of foundational high throughput assays to monitor neuronal morphology, mitochondrial function and electrophysiology, using high content screening and multi-electrode array formats. They have conducted high-throughput drug screens on muscular dystrophy patient cells, hiPSC-derived cardiomyocytes and hiPSC-derived neurons, including from Alzheimer’s patient specific hiPSC. Bang is a principal investigator for the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) National Cooperative Reprogrammed Cell Research Groups consortium, and also receives research support from rare disease foundations and pharma sponsored collaborations.
Anne Bang’s Research Report
Publications
- High content screen for compounds that modulate neurite outgrowth and retraction of human induced pluripotent stem cell derived neurons. Sherman, S.P. and A.G. Bang. Dis Model Mech. 2018 Feb 2;11(2):dmm031906.
- AAV-Mediated Mini-Agrin Delivery is Unable to Rescue Disease Phenotype in a Mouse Model of Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Type 2I. Vannoy, C.H., H. Zhou, C. Qiao, X. Xiao, A.G. Bang*, Qi L. Lu* Am J Pathol. 2017 Feb;187(2):431-440. (*corresponding authors).
- Neuronal medium supporting physiological synaptic activity and fundamental functions of human neurons in vitro. Bardy C., M. Van Den Hurk, C. March and, T. Eames, R. Hernandez, M. Kellogg, M. Gorris, B. Galet, V. Palomares, J. Brown, A.G. Bang, J. Mertens, L. Boehnke, L. Boyer, S. Simon, F. H. Gage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 May 19;112(20):E2725-34.
- A Scalable System for Production of Functional Pancreatic Progenitors from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Schulz T., H.Y. Young, A.D. Agulnick, J. Babin, E.E. Baetge, A.G. Bang, A. Bhoumik, et al. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37004.
- Novel surface markers for the isolation and transplantation of pancreatic cells derived from human embryonic stem cells. Kelly O.G., M.Y. Chan, L.A. Martinson, K. Kadoya, T. Ostertag, K. Ross, M. Richardson, M.K. Carpenter, K.A. D’Amour, E. Kroon, M. Moorman, E.E. Baetge, and A.G. Bang. Nat Biotechnol. 2011 Jul 31;29(8):750-6.
- Characteristics and characterization of human pluripotential stem cells. Bang A.G. and M.K. Carpenter. In Essentials of Stem Cell Biology, 2009 Nov 30;(38)339-343
- Deconstructing pluripotency. Bang A.G. and M.K. Carpenter. Science 2008 Apr 4;320(5872):58-9.
- Pancreatic endoderm derived from human embryonic stem cells generates glucose responsive insulin-secreting cells in vivo. Kroon E., L. A. Martinson, K. Kadoya, A.G. Bang, O.G. Kelly, S. Eliazer, H. Young, M. Richardson, N.G. Smart, J. Cunningham, A.D. Agulnick, D’Amour KA, M.K. Carpenter & E.E. Baetge. Nat Biotechnol. 2008 Apr;26(4):443-52.
- Production of pancreatic hormone-expressing endocrine cells from human embryonic stem cells. D’Amour K.A,. A.G. Bang, S. Eliazer, O.G. Kelly, A.D. Agulnick, N.G. Smart, M.A. Moorman, E. Kroon, M.K. Carpenter & E.E. Baetge. Nat Biotechnol. 2006 Nov;24(11):1392-401
Patents
- Jackson, M., and Bang, A.G. 2013. Theranostics platform and methods of use, Patent Application No. PCT/US13/26448, Sanford Burnham Medical Research Institute, La Jolla, CA.
- Kelly, O.G., and Bang, A.G. 2012. Methods for purifying endoderm and pancreatic endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cells, United States Patent 8,338,170, ViaCyte, Inc., San Diego, CA.
- D’Amour K., Bang A., Baetge, E. 2012. Endocrine precursor cells, pancreatic hormone-expressing cells and methods of production. United States Patent 8,129,182, ViaCyte, Inc., San Diego, CA.
- Green, C., Yu X., Bang A., Brandon, E., Kelly, O., Agulnick, A., Baetge, E., D’Amour K., Schulz, T., Robins, A. 2011. Stem cell aggregate suspension compositions and methods of differentiation thereof. United States Patent 8,008,075, ViaCyte, Inc., San Diego, CA.
 Dec 12, 2025
Dec 12, 2025Sanford Burnham Prebys scientists garner eight cancer research grants from Curebound to advance therapeutic treatments and cures
Dec 12, 2025Ten scientists at Sanford Burnham Prebys Medical Discovery Institute were awarded eight grants yesterday from Curebound, a San Diego-based philanthropic organization
 Oct 11, 2024
Oct 11, 2024Anne Bang joins $12.7M research project on the genetic basis of autism and schizophrenia
Oct 11, 2024Sanford Burnham Prebys scientist and an international team are funded by the California Institute for Regenerative Medicine.
 Aug 18, 2022
Aug 18, 2022Using stem cells to study the biochemistry of learning
Aug 18, 2022A method for studying human neurons could help researchers develop approaches for treating Alzheimer’s, schizophrenia and other neurological diseases.
 Dec 8, 2020
Dec 8, 2020What scientists are learning about COVID-19 and the brain
Dec 8, 2020We caught up with cell biologist Anne Bang, who recently teamed up with her husband to study how SARS-CoV-2 affects…
 Feb 7, 2019
Feb 7, 2019Drug screen conducted at Sanford Burnham Prebys identifies new therapeutic avenues for Alzheimer’s disease
Feb 7, 2019A screen of more than 1,600 Food and Drug Administration (FDA)–approved drugs performed at SBP’s Conrad Prebys Center for Chemical
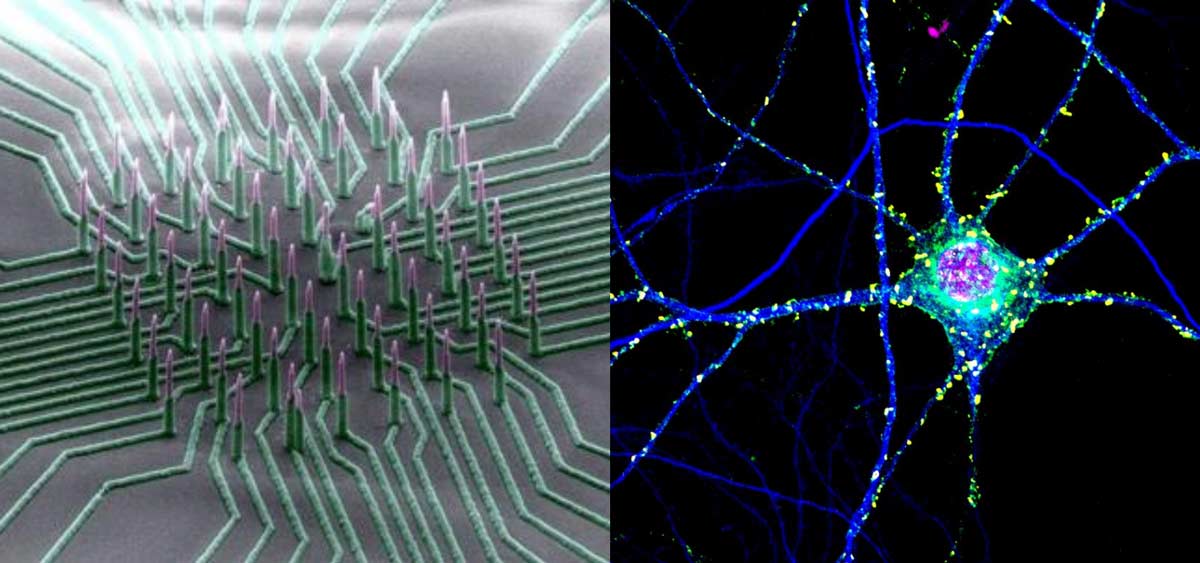 Apr 12, 2017
Apr 12, 2017Nanowire arrays allow electrical recording of neuronal networks
Apr 12, 2017To examine a neuron’s health, activity and response to drugs, scientists record its electrical activity. Current methods of recording are