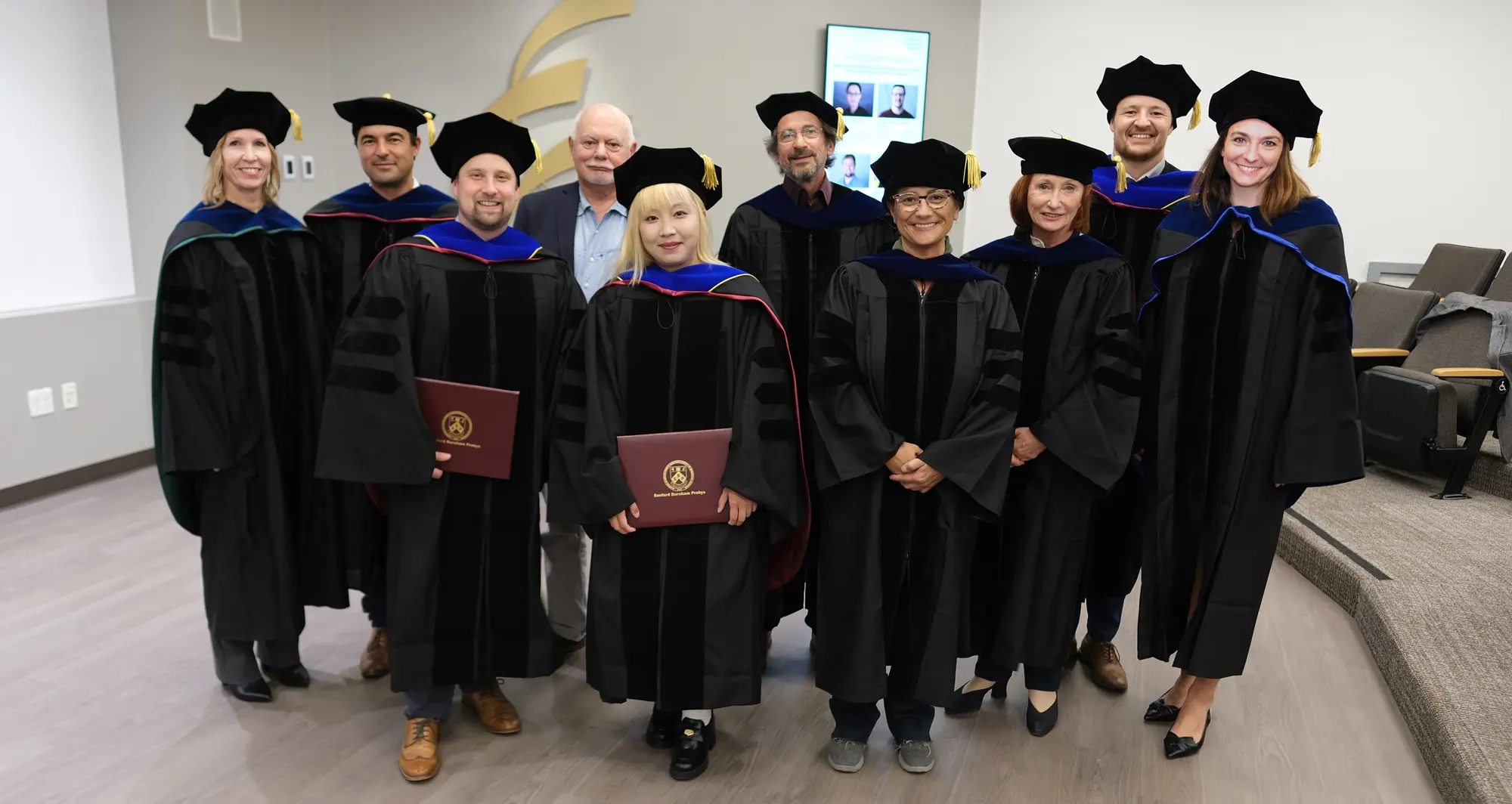
The Institute’s Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences held its second Commencement ceremony to celebrate four recent graduates
Family, friends and colleagues gathered at the end of May 2025 to applaud the four newest alumni of the Sanford Burnham Prebys Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. These early-career scientists are the latest graduates to leave their mark on the institute and carry forth the graduate program’s motto, “Knowledge is the power to heal.”
On Friday, May 30, 2025, the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences held its graduation ceremony at the institute’s La Jolla campus in the Victor E. LaFave III Memorial Auditorium.
“Each of you has made significant contributions to your field of science, created new knowledge and demonstrated the ability to perform independent research,” said Alessandra Sacco, PhD, dean of the institute’s graduate school and professor and director of the Development, Aging and Regeneration Program in the Center for Cardiovascular and Muscular Diseases.
“Today, we celebrate not only your academic journey, but also your years of dedication to get to this point, and the perseverance and intellectual curiosity that enabled you to reach this milestone.”
Following her remarks, Sacco introduced Ryan Loughran, PhD ’24, to speak on behalf of his fellow graduates.
“Graduate school is an experience unlike any other,” said Loughran. “You’re constantly drinking from a fire hose, learning new techniques, running experiments, coding data pipelines, writing and reviewing papers, preparing posters and giving talks.
‘I came to realize that it’s overwhelming by design. Somewhere in that chaos, something incredible happens. You’re forged by the fire. You begin to absorb information with an insatiable hunger. You think more critically and more creatively when confronting problems, and that is the true gift of the PhD experience.”
Loughran turned the podium over to Guy Salvesen, PhD, the inaugural dean of the graduate school, who provided the Commencement address.
“The graduates in front of you display the success of the program,” he said. “More importantly and more fundamentally, though, they have reached this milestone based on the merits of the hard-won accomplishments that they share with their mentors.”
Diane Klotz, PhD, chief learning officer at Sanford Burnham Prebys, then discussed the meaning of the hoods and symbols that are used in Commencement ceremonies. She invited the graduates forward and instructed faculty members to adorn them with the doctoral academic hoods signifying completion of a PhD program.
This year, the following graduates were recognized:
- Zong Ming Chua, PhD ’24, who trained in the Adams lab and was unable to attend the ceremony
- Jordan Friedlein, PhD ’24, who trained in the Bagchi lab and was hooded by Anindya Bagchi, PhD, an associate professor in the Cancer Genome and Epigenetics Program
- Ryan Loughran, PhD ’24, who trained in the Emerling lab and was hooded by Brooke Emerling, PhD, the director and an associate professor in the Cancer Metabolism and Microenvironment Program
- Zhouting Zhu, PhD ’24, who trained in the Rana lab and was hooded by Cosimo Commisso, PhD, the interim director and deputy director of the institute’s NCI-Designated Cancer Center and a professor in the Cancer Metabolism and Microenvironment Program
Andrei Osterman, PhD, the graduate school’s vice dean and associate dean of curriculum and a professor in the Center for Metabolic and Liver Diseases, provided the ceremony’s closing remarks.
“While today is primarily a celebration of individual intellectual achievements, it also recognizes your meaningful contributions to and interactions with the scientific community,” he said. “You have grown through peer review and collaborating with others, and these experiences will benefit you wherever your career takes you.”
More on this year’s graduates
Zong Ming Chua, PhD ’24, was born in Singapore. He developed a deep and early interest in biology after reading Darwin’s seminal work “On the Origin of Species” and various books by Richard Dawkins.
At Sanford Burnham Prebys, Zong Ming investigated the mechanisms that link cellular senescence and epigenetics. He discovered a new role of the histone variant H2A.Z R80C. He found that the histone variant influenced the transcriptomic profile of senescent cells.
Zong Ming moved to the Bay Area after graduating and is currently a computational biologist at GigaGen.
Jordan Friedlein, PhD ’24, was born and raised in Minnesota. From an early age, he expressed a desire to understand how the world worked. In high school, biology and physiology were his favorite classes.
Jordan joined the Bagchi Lab in 2019 and worked on investigating the role of circular RNA derived proteins in Myc-driven cancers. During his five years, Jordan enjoyed contributing to cutting-edge research and building lasting relationships with other grad students and institute members.
Ryan Loughran, PhD ’24, was born and raised in Greensburg, Penn. Growing up in a family with four generations of pharmacists, Ryan always imagined following in their footsteps and taking over the family-owned Loughran’s Pharmacy.
However, his path took a different turn during his undergraduate studies when he had the opportunity to spend a summer in New York City as an intern in the Emerling lab at Weill Cornell Medicine. He later moved with Emerling to help establish her new lab at Sanford Burnham Prebys as her lab manager. He later joined the Emerling lab as a graduate student.
Ryan plans to undertake a short postdoctoral position before transitioning into the pharmaceutical industry, where he aims to apply his knowledge and experience in cancer research to real-world applications.
Zhouting Zhu, PhD ’24, grew up in Changzhou city in the Jiangsu province of China. After completing a Master of Science in Surgery degree from Nanjing University in 2018, Zhouting joined the graduate program at Sanford Burnham Prebys.
She conducted her doctoral research in the lab of Tariq Rana, PhD, an educational affiliate professor in the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. Zhouting focused on RNA biology and cancer immunotherapy. Her work explored immune cell dynamics in tumors and spleens under various treatment conditions in mouse cancer models.
Zhouting is currently working toward MD-equivalency certification, with the long-term goal of becoming a board-certified physician-scientist.