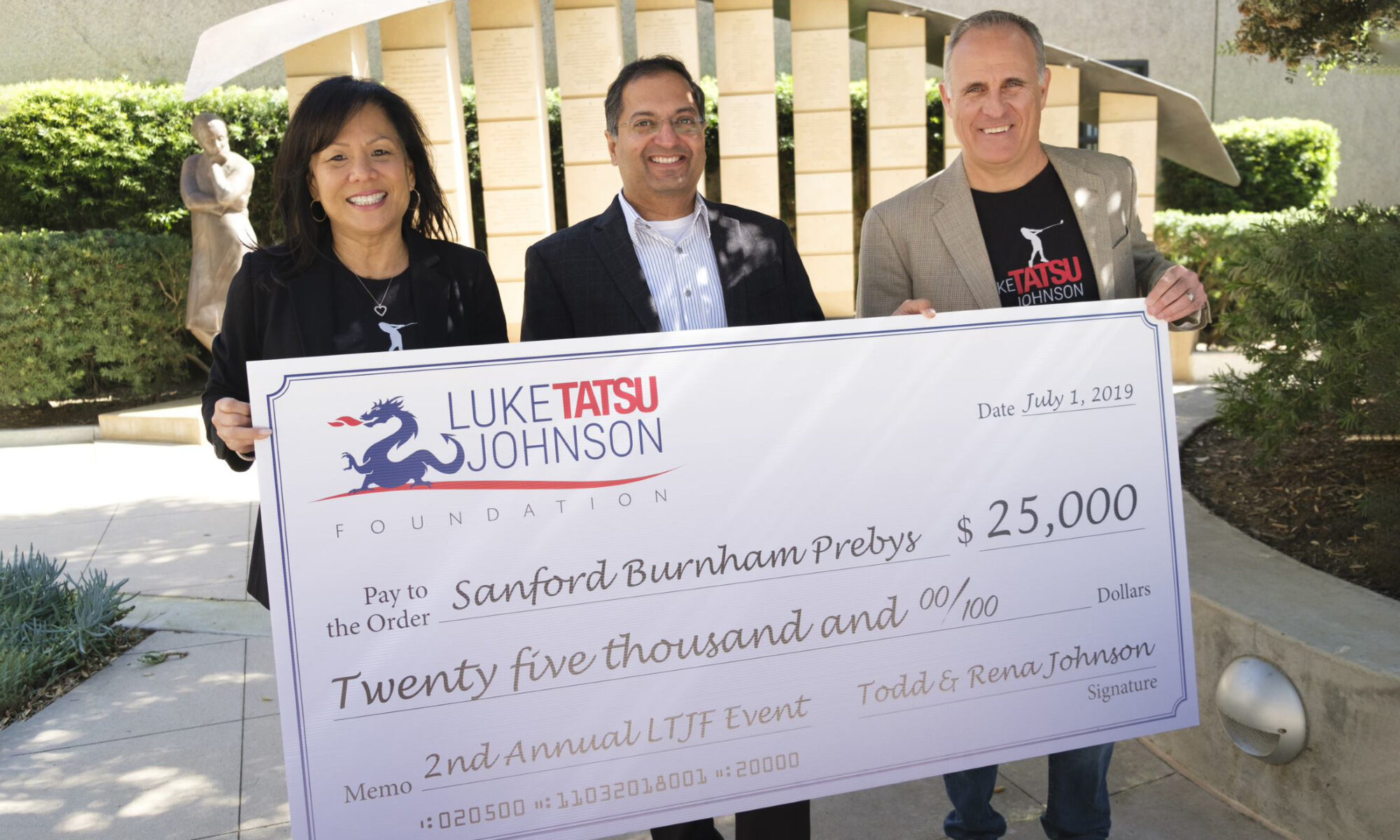
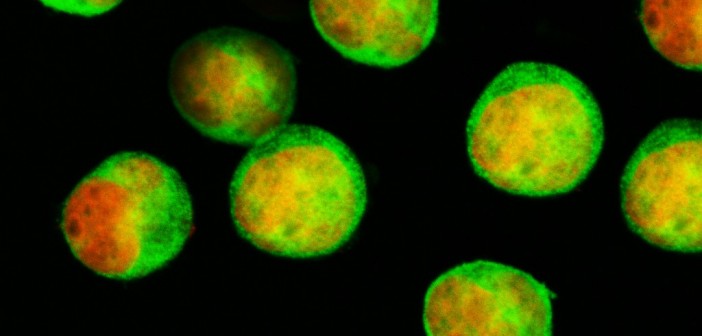
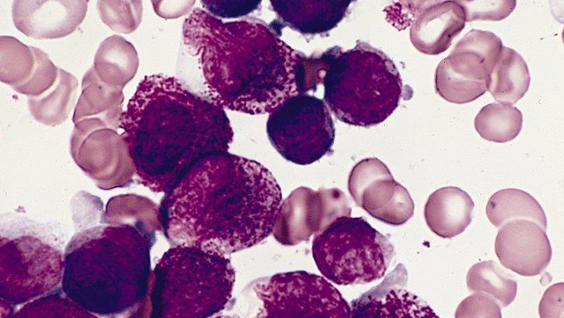
Since 2020, Todd and Rena Johnson, co-founders of the Luke Tatsu Johnson Foundation (LTJF), have helped fund the research of Associate Professor Ani Deshpande, PhD
But it all started with their son Luke. He had a very rare subtype of acute myeloid leukemia, one of the most difficult-to-treat cancers, and, sadly, he passed away from the disease in 2016. This inspired the Johnsons to become involved with fundraising and advocacy for cancer research.
“Our foundation started with a fundraising golf tournament to honor Luke, and that was about taking something so horrific and so horrible and finding a way to turn it into something positive,” says Rena. “If you can take that tragedy and put a positive spin on it, then everything around Luke and his name and his memory becomes positive.”
How “the stars and planets aligned” to bring the Johnsons to the Institute
In a remarkable coincidence, the Johnsons discovered on their first visit to the Institute that Deshpande’s research focuses on AF10 fusion AML, an extremely rare subtype of the disease that accounts for about 5 percent of cases. It’s also the subtype of AML that Luke had.
“It was a goosebumps-raising moment,” says Todd. “Once we visited Ani and saw his lab, we realized there was a lot more in common with our story and his research than we had realized before.”
“The stars and planets aligned and brought us to Ani,” adds Rena.
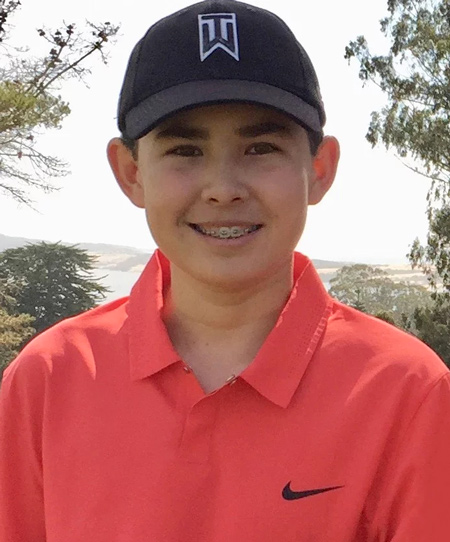

Luke Tatsu Johnson
As well as helping fund Deshpande’s research through LTJF and their partnership with the Rally! Foundation, the Johnsons are also on the Community Advisory Board (CAB) for the Institute’s Cancer Center, which advocates for cancer research by engaging the community.
“The CAB does such a wonderful job of connecting the community with the scientists, and we’re so excited to be involved in that,” says Todd. “That’s fundamentally what we do as a foundation—we support the folks doing this work so that children and families down the road can have a different outcome from Luke’s.”
AML research “needs more support and needs more funding”
The Johnsons’ support helped the AML research team discover a new potential treatment for AML, which is currently in preclinical studies, after which they hope it will advance to clinical trials. The research team maintains that it would have been impossible to secure the NIH grants necessary to do these studies without the jump start given by the LTJF and the Rally! Foundation.
“We couldn’t do what we do without the Johnsons’ support,” says Deshpande. “We are so grateful to have them in our corner, and we’re confident that our work will help improve outcomes for kids like Luke down the line.”
Despite this progress, more research into AML and other leukemias is still needed. Leukemia is the most common cancer in children and teens. About 4,000 children are diagnosed with leukemia each year, and AML accounts for about a third of these cases.
Studying AML from all angles
To tackle this pressing problem, the Institute has established an AML disease team composed of researchers across labs and clinician partners. The team’s research falls into several large categories, including studying the genetics of AML, studying how the disease works in animal models and working to develop drugs that can target specific mutations associated with the disease, which are numerous.
“AML has many different subtypes, so it’s been difficult for researchers to make major advances to treat all cases of AML,” says Deshpande, who co-leads the AML team with Professor Peter D. Adams, PhD “Most patients with AML are given the same treatments that have been used since the ’70s, which is why we want to look at AML from as many angles as possible.”
In addition to being difficult to treat, it is also challenging to get funding for AML research, particularly for the rarer subtypes. This makes the support of foundations such as LTJF even more vital to researchers like Deshpande.
“This is exactly why AML research needs more support and needs more funding, because this is a much more difficult disease than other forms of leukemia,” says Todd. “Many patients don’t have positive outcomes, and the only way to turn that pendulum is to intensify our efforts and increase the amount of research being done.”